Details
PVC SHEETS
PVC Sheets, also called Polyvinyl Chloride Sheets, are flat, semi-rigid or flexible plastic sheets made from PVC polymer, a synthetic thermoplastic composed of vinyl chloride monomers. PVC sheets are produced via extrusion, calendering, or compression molding and are available in rigid (uPVC/RPVC) or flexible forms (with added plasticizers). Known for their durability, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy, PVC sheets are widely used in construction, healthcare, signage, and industrial applications.
Chemical Composition of PVC
PVC is composed of polyvinyl chloride resin, with additional stabilizers, plasticizers, and additives to enhance properties such as flexibility, UV resistance, and impact strength. It is available in two primary forms: rigid (uPVC - unplasticized PVC) and flexible (plasticized PVC).
Key Features:
High Strength and Durability – Resistant to mechanical stress and impact.
Excellent Chemical Resistance – Resistant to acids, alkalis, salts, and many industrial chemicals.
Good Flame Retardancy – Self-extinguishing properties make it safe for construction and electrical applications.
Water & Moisture Resistance – Non-absorbent, making it ideal for wet or humid environments.
Electrical Insulation – A good dielectric material, used in electrical applications.
Weather & UV Resistance – Certain PVC sheets are UV stabilized for outdoor applications.
Corrosion Resistance – Suitable for environments with exposure to chemicals and weather conditions.
Ease of Fabrication – Can be cut, welded, bonded, drilled, and thermoformed easily.
Cost-Effective – An affordable alternative to metal and other plastic materials.
Types:
PVC sheets come in various types, each designed for specific applications:
A. Rigid PVC Sheets (uPVC - Unplasticized PVC)
-Hard and durable, with excellent mechanical properties.
-Used for construction, industrial components, and electrical enclosures.
-Resistant to impact, UV, and chemicals.
B. Flexible PVC Sheets
-Contains plasticizers, making them softer and more flexible.
-Used for curtains, flooring, and waterproofing applications.
-Good resistance to abrasion and chemicals.
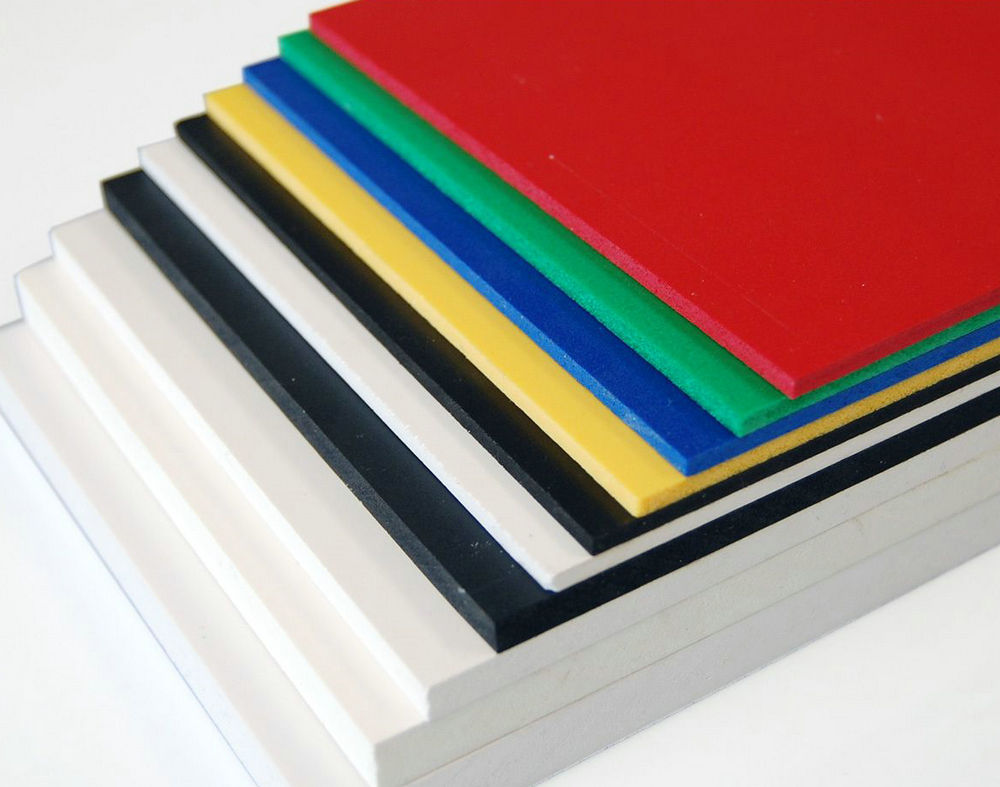
C. Foam PVC Sheets (Expanded PVC / PVC Forex / PVC Celuka)
-Lightweight and rigid, with a smooth, matte surface.
-Commonly used for signage, advertising boards, and exhibition panels.
-Good printability and easy to cut or shape.
D. Clear PVC Sheets (Transparent PVC)
-High optical clarity and impact resistance.
-Used for windows, machine guards, and protective barriers.
E. High-Impact PVC Sheets
-Modified with additives for greater impact resistance.
-Used in high-wear applications such as automotive parts and safety shields.
F. PVC Laminated Sheets
-Laminated with decorative films or coatings.
-Used for furniture, interior decorations, and doors.

Technical Parameters:
Here are the common technical properties of PVC sheets. The values may vary depending on the grade:
Property | Typical Value |
Density | 1.35 – 1.45 g/cm³ |
Tensile Strength | 50 – 80 MPa |
Impact Strength | 2 – 10 kJ/m² |
Hardness (Shore D) | 75 – 85 |
Water Absorption | < 0.1% |
Flammability | Self-extinguishing (UL 94 V-0) |
Service Temperature Range | -20°C to 60°C |
Thermal Conductivity | Low (good insulation properties) |
Electrical Insulation | High |
Product Benefits:
High Durability & Longevity
-Resistant to mechanical damage, moisture, and UV degradation.
Lightweight & Easy to Handle
-Rigid yet lightweight, making it easy to transport and install.
Chemical & Corrosion Resistance
-Does not corrode, making it ideal for industrial and marine applications.
Fire Retardant Properties
-Self-extinguishing nature makes it safer than many other plastics.
Weather & Water Resistance
-Perfect for outdoor and marine environments.
Versatile Processing & Fabrication
-Can be cut, welded, glued, or thermoformed for various applications.
Cost-Effective & Sustainable
-Affordable compared to metals and some other polymers.
Applications:
PVC sheets are used in a wide range of industries, including:
Construction & Building
-Wall cladding, ceiling panels, partitions, and doors.
-Roofing and waterproofing applications.
Industrial Applications
-Chemical-resistant tanks, pipes, and ducting.
-Machine guards, work surfaces, and enclosures.
Automotive & Transportation
-Interior panels, trims, and protective covers.
Advertising & Signage
-Billboards, display boards, and digital printing surfaces.
Electrical & Electronics
-Insulation panels, electrical enclosures, and switchgear covers.
Home & Interior Design
-Decorative wall panels, laminated sheets, and kitchen cabinets.
Marine Applications
-Boat interiors, deck covers, and waterproof flooring.
Storage & Handling:
To maintain PVC sheet quality, follow these storage guidelines:
-Keep in a dry, cool area, away from direct sunlight to prevent UV degradation.
-Store horizontally to avoid warping or bending.
-Avoid stacking heavy objects on top of stored PVC sheets.
-Use protective covers to prevent scratches and contamination.
FAQ
Q1: What is the difference between rigid and flexible PVC sheets?
A: Rigid PVC is hard, durable, and impact-resistant, while flexible PVC is softer and bendable due to added plasticizers.
Q2: Can PVC sheets be painted?
A: Yes, PVC sheets can be painted using acrylic-based paints or special plastic primers.
Q3: How are PVC sheets cut and machined?
A: They can be cut using saws, routers, and CNC machines. Drilling and welding are also possible.
Q4: How do I clean and maintain PVC sheets?
A: Use a mild detergent and soft cloth. Avoid abrasive cleaners to prevent scratching.
Q5: Can PVC sheets be thermoformed?
A: Yes, they can be heated and molded into various shapes.
Q6: Can PVC sheets be used outdoors?
A: Only UV-stabilized grades are suitable for prolonged outdoor use (e.g., signage, roofing).
Q7: What chemicals damage PVC?
A: Avoid ketones (e.g., acetone), aromatic hydrocarbons (e.g., benzene), and concentrated acids.
Q8: Why does flexible PVC become brittle over time?
A: Plasticizers can migrate out, especially in heat or sunlight. Use UV/heat-stabilized grades.
Q9: What are the advantages of PVC Sheets over competing material, such as PET, PP, PE, WOOD and Metals?
A:
vs. PET: Better flame retardancy and chemical resistance.
vs. Polypropylene (PP): Higher rigidity and UV resistance.
vs. Polyethylene (PE): Superior dimensional stability and strength.
vs. Wood: Moisture-resistant, rot-proof, and termite-proof.
vs. Metals: Non-corrosive, lightweight, and electrically insulating.
- PRE: No more
- NEXT: No more